Pointtax as a Solution to Tax Evasion and Budget Deficits
by JuanNovember 17, 2019 7 minutes • 1282 words
Table of contents
Update June 2020: In 2015, our model predicted a huge global crisis starting in 2019 to be felt many years afterwards. This is now known as the Covid-19 pandemic. Our model predicts inflation next, as a result of governments applying sophistical mercantile solutions, now known as “bailouts”, on supply and demand problems. These bailouts will be paid for by either inflation (as college debt, rising bills, rent, etc) or by increased taxation, both will lead to unrest (as seen in the US riots) or a change in government. Here, we propose the proper solution to those future new governments for them to not make the mistakes of the current ones.
Pointtax is a points-based taxation system that follows Adam Smith’s four taxation maxims , derived from Book 5 Chapter 2 of The Wealth of Nations .
The taxation of modern Economics suffers from two problems:
| Problem | Effect |
|---|---|
| Taxes are imposed not on where they are meant to be | For example, a sales tax is meant to burden the merchant. However, he merely transfers it to the consumer and so the consumer is burdened more than the merchant |
| Taxes must only be paid in money | Sellers must have money available to pay the tax. This forces them to sell their goods or services for money (which may not be his primary skill) |
We correct these problems through a system called Points Taxation or Pointtax. This system levies taxes directly on the points that are gained in a points-based economic system .
The points represent the value of goods and services that are assigned by its seller (points-giver) from his own perspective. Unlike money which is a legal tender or currency, points are only a store of value and are only meant for bilateral exchanges with a few people that the seller wants.
.What was the problem with the Economic or Commercial system of taxation?
The Commercial system only allows money for transactions. This means if you are a banana farmer then you must sell your bananas for money to pay a money-tax, such as a property tax.
In the past, before the Europeans colonized the world, the payment of taxes could be done by labor (as forced-labor poll taxes) or by kind. The farmer could just deliver his produce to the chieftain or king and not have to go through a layer of merchants who might give a disadvantageous price for them.
After the Commercial system was formalized, the king no longer cared about the farmers, but on the money that he collected from them. This can be seen in our modern taxation system which follows these steps:
- Total revenue is determined
- Deductions are removed to arrive at the taxable revenue
- A tax is computed on the taxable revenue depending on tax laws
- The tax is paid by whoever filed the tax (such as withholding taxes) which must be within the deadline
- Mistakes in the process result in penalties or tax credits
Because of this, taxation in Economics has two quirks:
- Taxes can only be paid in money. A tax payment in bananas that can only be harvested 1 month before the tax payment day, will be rotten by tax day.
- Taxes are based on the value transacted without caring who ultimately pays for it. A corporate filer might get some tax savings but not give those savings back to its people.
This causes problems:
- A taxpayer must have ready money to pay the tax even if his revenue payment might be delayed. This forces him to get expensive cash credits or loans, adding to his costs
- The tax burden is usually transferred to the people, adding to the burden of society. Workers and customers usually rely on the company to file taxes for their behalf. The company could then cheat and not remit all of the taxes, leading totax avoidance and evasion.
Since the taxation system only cares about values, the burden of identifying where those values came from must be furnished by the taxpayer. This manifests as the lengthy filing of Income Tax Returns.
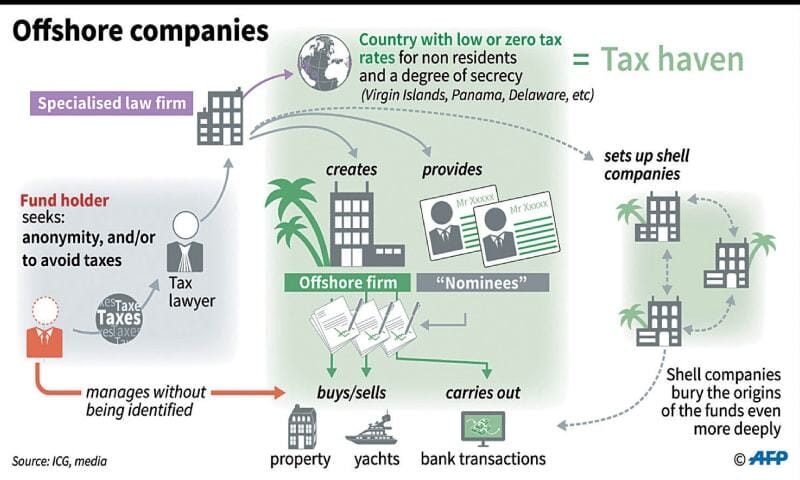
Because of this, taxation becomes unnecessarily burdensome and leaky, causing people to avoid it as much as possible while providing less-than-optimal revenue. In addition, the complexity of taxation leads to tax loopholes and tax havens.
All of these then leads to lower tax revenues and higher budget deficits, weaking government and reducing the infrastructure and services available to the people, even causing governments to privatize its most essential parts. America now has a $22 trillion debt and its government shuts down parts of itself more often.
Our Solution: Points-taxation system
Our solution is a new process that factors in the nature of the revenue and the people involved in generating that revenue, either as a buyer party or a seller party:
- Everyone values their goods or services for sale in points which is pegged to grains. For example, 1 point = 1 kg of rice
- Put all points-transactions in a centralized system, such as an ecommerce platform
- Categorize all transactions as based on either labor, professional-services, raw materials, basic goods, finished products, luxuries, etc. and assign each item in the transaction a proper tax rate
- The government transfers the appropriate points to itself and claims the value when the points are accumulated
This system can work totally offline with pen, paper, and seals since it was proposed by Adam Smith in the 18th century. This system has the following advantages:
- The points are not legal tender, but are merely the store of value. It is a measure of personal worth instead of universal value. This makes the tax authorities not inclined to corrupt the tax collection – who would want to amass a tax revenue of potatoes or professional singing?
- Since the points represent personal worth, then the taxpayer will be more willing to pay taxes since it is in his produced goods and services, not in money. Tax evasion and avoidance naturally become less common.
- Tax filing and payment can be automated if the transactions will be done online, and there is no need to arrive at the net taxable revenue.
Taxation Crosses Over Onto Politics
Pointtax can serve as the stepping stone towards a regulated democratic system wherein only the taxpayers are allowed to vote for the leaders who will spend those taxes.
Mini-FAQ
1. How are Pantry Points different from Simbi and barter points?
Simbi are not pegged to anything and are as arbitrary as fiat. Because it is arbitrary, it cannot be used for taxation or even as a consistent store of value. This makes it more similar to cryptocurrency.
Barter points are pegged to fiat which is also arbitrary. In fact, switching from fiat to barter-based-on-fiat is sticking with the same flawed system without gaining any advantage. This is why systems with barter and barter-points fail.
2. How are Pantry Points different from Cryptocurrency?
Aside from being based on nothing, cryptocurrency is tradeable with anyone. This makes it easy to spread crytobubble-crises, which is the opposite of our goal of making a resilient economic system.